- Sort Score
- Num 10 results
- Language All
Results 101 - 110 of 490 for declares (0.07 seconds)
-
docs/es/docs/tutorial/schema-extra-example.md
# Declarar Ejemplos de Request { #declare-request-example-data } Puedes declarar ejemplos de los datos que tu aplicación puede recibir. Aquí tienes varias formas de hacerlo. ## Datos extra de JSON Schema en modelos de Pydantic { #extra-json-schema-data-in-pydantic-models } Puedes declarar `examples` para un modelo de Pydantic que se añadirá al JSON Schema generado. //// tab | Pydantic v2Created: Sun Dec 28 07:19:09 GMT 2025 - Last Modified: Tue Dec 16 16:33:45 GMT 2025 - 10.3K bytes - Click Count (0) -
docs/es/docs/tutorial/dependencies/classes-as-dependencies.md
//// tab | Python 3.9+ sin `Annotated` /// tip | Consejo Prefiere usar la versión `Annotated` si es posible. /// ```Python commons: CommonQueryParams = Depends() ``` //// Declaras la dependencia como el tipo del parámetro, y usas `Depends()` sin ningún parámetro, en lugar de tener que escribir la clase completa *otra vez* dentro de `Depends(CommonQueryParams)`. El mismo ejemplo se vería entonces así:
Created: Sun Dec 28 07:19:09 GMT 2025 - Last Modified: Wed Dec 17 20:41:43 GMT 2025 - 7.1K bytes - Click Count (0) -
docs/es/docs/tutorial/path-params.md
Si te estás preguntando, "AlexNet", "ResNet" y "LeNet" son solo nombres de <abbr title="Técnicamente, arquitecturas de modelos de Deep Learning">modelos</abbr> de Machine Learning. /// ### Declarar un *path parameter* { #declare-a-path-parameter } Luego crea un *path parameter* con una anotación de tipo usando la clase enum que creaste (`ModelName`): {* ../../docs_src/path_params/tutorial005_py39.py hl[16] *}
Created: Sun Dec 28 07:19:09 GMT 2025 - Last Modified: Wed Dec 17 20:41:43 GMT 2025 - 9.8K bytes - Click Count (0) -
docs/fr/docs/tutorial/background-tasks.md
* Les arguments nommés à passer à la fonction de tâche (`message="some notification"`). ## Injection de dépendances Utiliser `BackgroundTasks` fonctionne aussi avec le système d'injection de dépendances. Vous pouvez déclarer un paramètre de type `BackgroundTasks` à différents niveaux : dans une *fonction de chemin*, dans une dépendance, dans une sous-dépendance...
Created: Sun Dec 28 07:19:09 GMT 2025 - Last Modified: Sat Oct 11 17:48:49 GMT 2025 - 5.5K bytes - Click Count (0) -
docs/pt/docs/advanced/additional-responses.md
Você pode declarar um `response_model`, utilizando o código de status padrão `200` (ou um customizado caso você precise), e depois adicionar informações adicionais para esse mesmo retorno em `responses`, diretamente no esquema OpenAPI. O **FastAPI** manterá as informações adicionais do `responses`, e combinará com o esquema JSON do seu modelo.
Created: Sun Dec 28 07:19:09 GMT 2025 - Last Modified: Wed Dec 17 20:41:43 GMT 2025 - 9.4K bytes - Click Count (0) -
docs/pt/docs/advanced/templates.md
$ pip install jinja2 ---> 100% ``` </div> ## Usando `Jinja2Templates` { #using-jinja2templates } * Importe `Jinja2Templates`. * Crie um objeto `templates` que você possa reutilizar posteriormente. * Declare um parâmetro `Request` no *path operation* que retornará um template.Created: Sun Dec 28 07:19:09 GMT 2025 - Last Modified: Wed Dec 17 20:41:43 GMT 2025 - 3.6K bytes - Click Count (0) -
docs/en/docs/advanced/custom-response.md
But if you return a `Response` directly (or any subclass, like `JSONResponse`), the data won't be automatically converted (even if you declare a `response_model`), and the documentation won't be automatically generated (for example, including the specific "media type", in the HTTP header `Content-Type` as part of the generated OpenAPI).
Created: Sun Dec 28 07:19:09 GMT 2025 - Last Modified: Wed Dec 17 20:41:43 GMT 2025 - 12.4K bytes - Click Count (0) -
docs/fr/docs/index.md
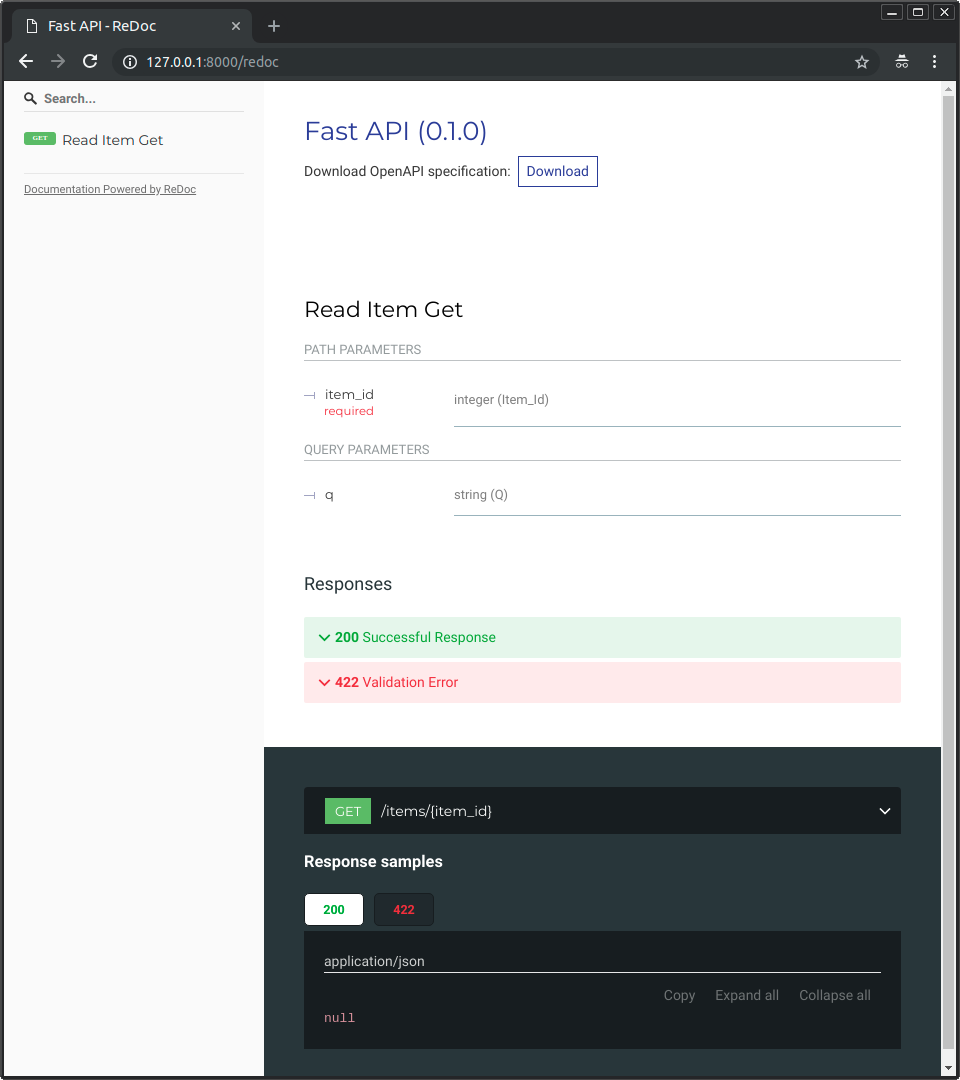 ## Exemple plus poussé Maintenant, modifiez le fichier `main.py` pour recevoir <abbr title="en anglais : body">le corps</abbr> d'une requête `PUT`. Déclarez ce corps en utilisant les types Python standards, grâce à Pydantic. ```Python hl_lines="4 9-12 25-27" from typing import Union from fastapi import FastAPI from pydantic import BaseModel
Created: Sun Dec 28 07:19:09 GMT 2025 - Last Modified: Sat Oct 11 17:48:49 GMT 2025 - 22K bytes - Click Count (0) -
docs/pt/docs/python-types.md
O Python possui suporte para "dicas de tipo" ou "type hints" (também chamado de "anotações de tipo" ou "type annotations") Esses **"type hints"** são uma sintaxe especial que permite declarar o <abbr title = "por exemplo: str, int, float, bool">tipo</abbr> de uma variável. Ao declarar tipos para suas variáveis, editores e ferramentas podem oferecer um melhor suporte.
Created: Sun Dec 28 07:19:09 GMT 2025 - Last Modified: Wed Dec 17 20:41:43 GMT 2025 - 16.7K bytes - Click Count (0) -
docs/es/docs/tutorial/response-model.md
Si tienes chequeos estrictos de tipos en tu editor, mypy, etc., puedes declarar el tipo de retorno de la función como `Any`. De esa manera le dices al editor que intencionalmente estás devolviendo cualquier cosa. Pero FastAPI todavía hará la documentación de datos, validación, filtrado, etc. con `response_model`. /// ### Prioridad del `response_model` { #response-model-priority }Created: Sun Dec 28 07:19:09 GMT 2025 - Last Modified: Wed Dec 17 20:41:43 GMT 2025 - 17.7K bytes - Click Count (0)