- Sort Score
- Result 10 results
- Languages All
Results 1 - 10 of 15 for stdio (0.02 sec)
-
api/maven-api-cli/src/main/java/org/apache/maven/api/cli/ParserRequest.java
Registered: Sun Sep 07 03:35:12 UTC 2025 - Last Modified: Sat Jun 07 06:22:47 UTC 2025 - 15.9K bytes - Viewed (0) -
docs/en/docs/tutorial/debugging.md
# Debugging { #debugging } You can connect the debugger in your editor, for example with Visual Studio Code or PyCharm. ## Call `uvicorn` { #call-uvicorn } In your FastAPI application, import and run `uvicorn` directly: {* ../../docs_src/debugging/tutorial001.py hl[1,15] *} ### About `__name__ == "__main__"` { #about-name-main } The main purpose of the `__name__ == "__main__"` is to have some code that is executed when your file is called with:Registered: Sun Sep 07 07:19:17 UTC 2025 - Last Modified: Sun Aug 31 09:15:41 UTC 2025 - 2.5K bytes - Viewed (0) -
api/maven-api-cli/src/main/java/org/apache/maven/api/cli/InvokerRequest.java
* * @return an {@link Optional} containing the input stream, or empty if not applicable */ @Nonnull default Optional<InputStream> stdIn() { return Optional.ofNullable(parserRequest().stdIn()); } /** * Returns the output stream for the Maven execution, if running in embedded mode. *Registered: Sun Sep 07 03:35:12 UTC 2025 - Last Modified: Wed Jun 11 13:14:09 UTC 2025 - 6.7K bytes - Viewed (0) -
okhttp/src/jvmMain/resources/okhttp3/internal/publicsuffix/PublicSuffixDatabase.list
studio.ca-central-1.sagemaker.aws studio.cn-north-1.sagemaker.com.cn studio.cn-northwest-1.sagemaker.com.cn studio.eu-central-1.sagemaker.aws studio.eu-north-1.sagemaker.aws studio.eu-south-1.sagemaker.aws studio.eu-south-2.sagemaker.aws studio.eu-west-1.sagemaker.aws studio.eu-west-2.sagemaker.aws studio.eu-west-3.sagemaker.aws studio.il-central-1.sagemaker.aws studio.me-central-1.sagemaker.aws
Registered: Fri Sep 05 11:42:10 UTC 2025 - Last Modified: Tue May 27 22:00:49 UTC 2025 - 129.6K bytes - Viewed (3) -
android-test/src/androidTest/README.md
$ echo "no" | avdmanager --verbose create avd --force --name "pixel5" --device "pixel" --package "system-images;android-29;google_apis;x86" --tag "google_apis" --abi "x86" ``` 2. Run an Emulator using Android Studio or from command line. ``` $ emulator -no-window -no-snapshot-load @pixel5 ``` 2. Turn on logs with logcat ```
Registered: Fri Sep 05 11:42:10 UTC 2025 - Last Modified: Fri Aug 22 08:12:58 UTC 2025 - 2.5K bytes - Viewed (0) -
okhttp/build.gradle.kts
afterEvaluate { tasks.withType<Test> { if (javaLauncher.get().metadata.languageVersion.asInt() < 9) { // Work around robolectric requirements and limitations // https://cs.android.com/android-studio/platform/tools/base/+/mirror-goog-studio-main:build-system/gradle-core/src/main/java/com/android/build/gradle/tasks/factory/AndroidUnitTest.java;l=339 allJvmArgs = allJvmArgs.filter { !it.startsWith("--add-opens") } }Registered: Fri Sep 05 11:42:10 UTC 2025 - Last Modified: Thu Jul 03 03:59:03 UTC 2025 - 9.4K bytes - Viewed (0) -
src/test/java/org/codelibs/fess/helper/ProcessHelperTest.java
} } public void test_sendCommand_withRunningProcess() { String sessionId = "test_send_command"; List<String> cmdList = Arrays.asList("cat"); // cat reads from stdin Consumer<ProcessBuilder> pbCall = pb -> { pb.redirectErrorStream(true); }; try { JobProcess jobProcess = processHelper.startProcess(sessionId, cmdList, pbCall);Registered: Thu Sep 04 12:52:25 UTC 2025 - Last Modified: Sat Jul 12 05:35:01 UTC 2025 - 15.1K bytes - Viewed (0) -
docs/en/docs/tutorial/body.md
There were even some changes to Pydantic itself to support this. The previous screenshots were taken with <a href="https://code.visualstudio.com" class="external-link" target="_blank">Visual Studio Code</a>. But you would get the same editor support with <a href="https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/" class="external-link" target="_blank">PyCharm</a> and most of the other Python editors:
Registered: Sun Sep 07 07:19:17 UTC 2025 - Last Modified: Sun Aug 31 10:58:56 UTC 2025 - 7.1K bytes - Viewed (0) -
docs/en/docs/features.md
You will rarely need to come back to the docs. Here's how your editor might help you: * in <a href="https://code.visualstudio.com/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Visual Studio Code</a>: 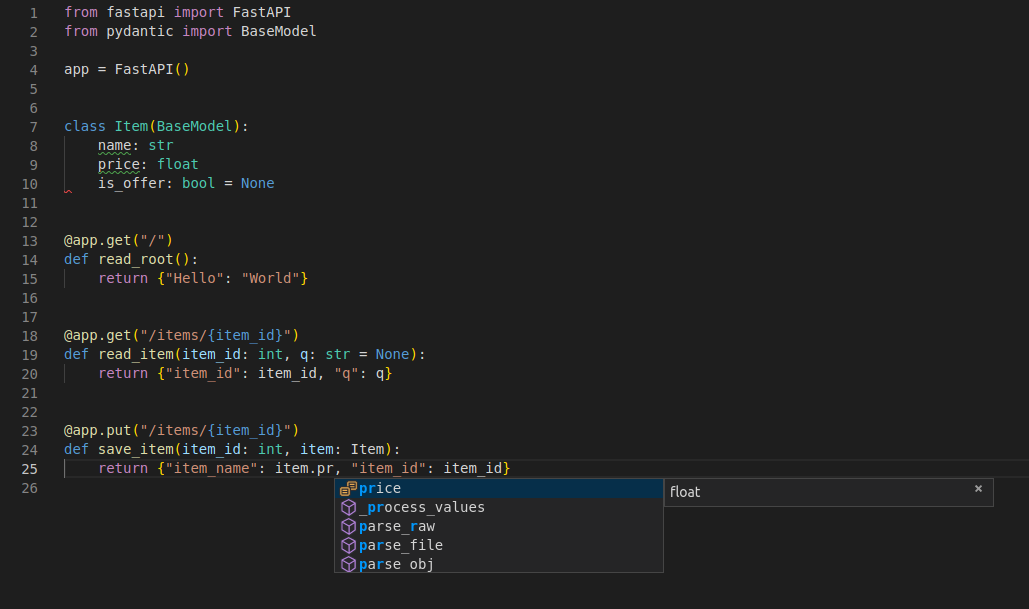 * in <a href="https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/" class="external-link" target="_blank">PyCharm</a>:
Registered: Sun Sep 07 07:19:17 UTC 2025 - Last Modified: Sun Aug 31 09:15:41 UTC 2025 - 9.5K bytes - Viewed (0) -
docs/en/data/external_links.yml
https://www.linkedin.com/in/mnrozhkov/ link: https://www.evidentlyai.com/blog/fastapi-tutorial title: ML serving and monitoring with FastAPI and Evidently - author: Visual Studio Code Team author_link: https://code.visualstudio.com/ link: https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/python/tutorial-fastapi title: FastAPI Tutorial in Visual Studio Code - author: Apitally author_link: https://apitally.io link: https://blog.apitally.io/fastapi-application-monitoring-made-easy title: FastAPI application monitoring...
Registered: Sun Sep 07 07:19:17 UTC 2025 - Last Modified: Sun Aug 31 10:49:48 UTC 2025 - 23K bytes - Viewed (0)