- Sort Score
- Result 10 results
- Languages All
Results 1 - 10 of 20 for it (0.02 sec)
-
docs/erasure/README.md
In 12 drive example above, with MinIO server running in the default configuration, you can lose any of the six drives and still reconstruct the data reliably from the remaining drives.
Registered: Sun Jun 16 00:44:34 UTC 2024 - Last Modified: Thu Sep 29 04:28:45 UTC 2022 - 4.1K bytes - Viewed (0) -
docs/integrations/veeam/README.md
## Prerequisites
Registered: Sun Jun 16 00:44:34 UTC 2024 - Last Modified: Thu Sep 29 04:28:45 UTC 2022 - 5.4K bytes - Viewed (0) -
docs/bucket/quota/README.md
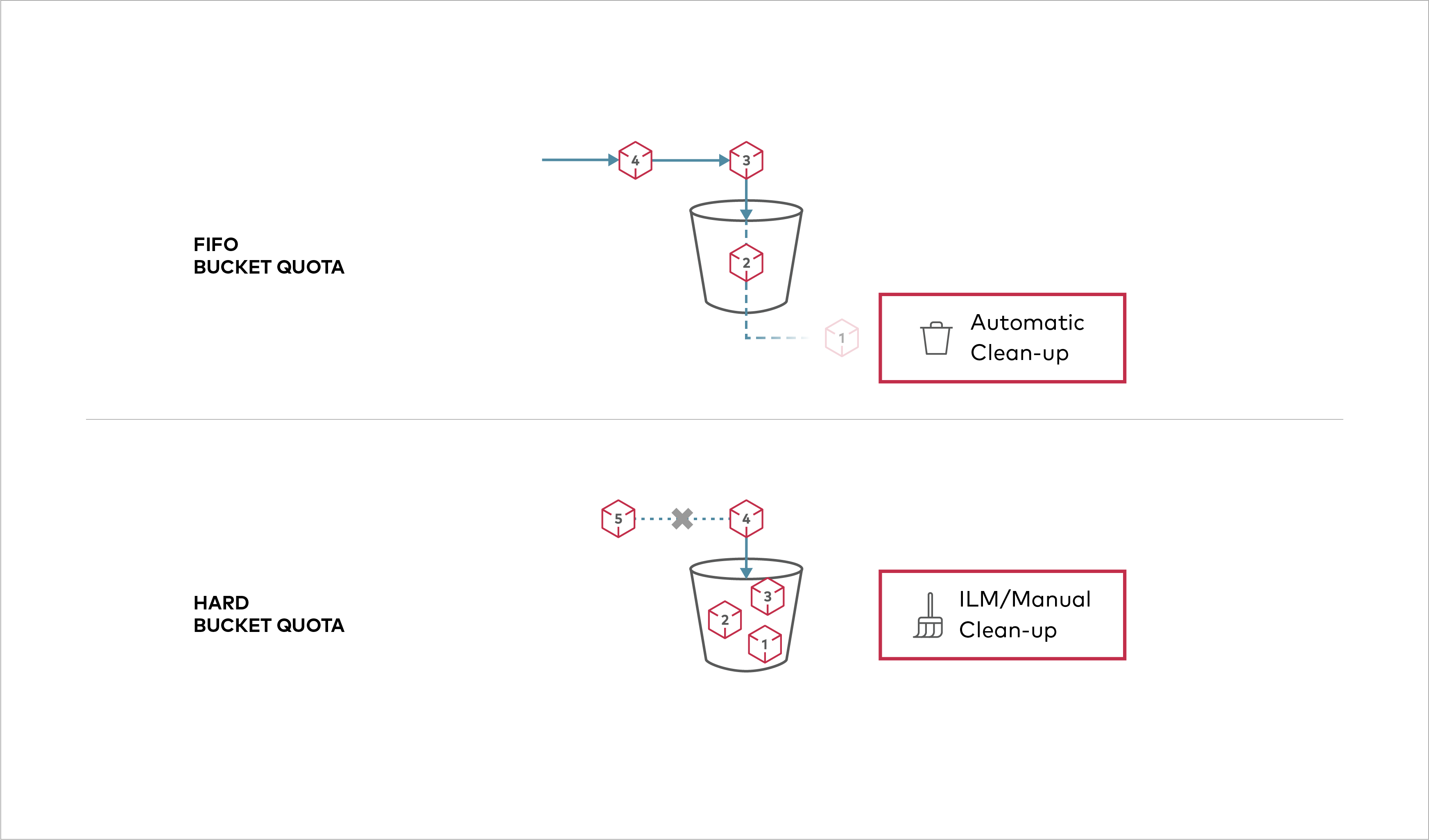 Buckets can be configured to have `Hard` quota - it disallows writes to the bucket after configured quota limit is reached. ## Prerequisites - Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html#procedure).
Registered: Sun Jun 16 00:44:34 UTC 2024 - Last Modified: Tue Oct 25 00:44:15 UTC 2022 - 1.1K bytes - Viewed (0) -
docs/erasure/storage-class/README.md
`STANDARD` storage class implies more parity than `REDUCED_REDUNDANCY` class. So, `STANDARD` parity drives should be - Greater than or equal to 2, if `REDUCED_REDUNDANCY` parity is not set. - Greater than `REDUCED_REDUNDANCY` parity, if it is set. Parity blocks can not be higher than data blocks, so `STANDARD` storage class parity can not be higher than N/2. (N being total number of drives)
Registered: Sun Jun 16 00:44:34 UTC 2024 - Last Modified: Tue Aug 15 23:04:20 UTC 2023 - 5.8K bytes - Viewed (0) -
docs/orchestration/README.md
MinIO is built ground up on the cloud-native premise. With features like erasure-coding, distributed and shared setup, it focuses only on storage and does it very well. While, it can be scaled by just replicating MinIO instances per tenant via an orchestration platform. > In a cloud-native environment, scalability is not a function of the application but the orchestration platform.
Registered: Sun Jun 16 00:44:34 UTC 2024 - Last Modified: Thu Sep 29 04:28:45 UTC 2022 - 2.2K bytes - Viewed (0) -
internal/grid/README.md
# MinIO Grid The MinIO Grid is a package that provides two-way communication between servers. It uses a single two-way connection to send and receive messages between servers. It includes built in muxing of concurrent requests as well as congestion handling for streams. Requests can be "Single Payload" or "Streamed". Use the MinIO Grid for: * Small, frequent requests with low latency requirements.
Registered: Sun Jun 16 00:44:34 UTC 2024 - Last Modified: Thu Jan 18 07:03:17 UTC 2024 - 9.4K bytes - Viewed (0) -
docs/distributed/README.md
**In our tests we also found ext4 does not honor POSIX O_DIRECT/Fdatasync semantics, ext4 trades performance for consistency guarantees. Please avoid ext4 in your setup.** **If MinIO distributed setup is using NFS volumes underneath it is not guaranteed MinIO will provide these consistency guarantees since NFS is not strictly consistent (If you must use NFS we recommend that you at least use NFSv4 instead of NFSv3 for relatively better outcomes).** ## Get started
Registered: Sun Jun 16 00:44:34 UTC 2024 - Last Modified: Thu Jan 18 07:03:17 UTC 2024 - 8.8K bytes - Viewed (0) -
docs/lambda/README.md
MinIO's Object Lambda, enables application developers to process data retrieved from MinIO before returning it to an application. You can register a Lambda Function target on MinIO, once successfully registered it can be used to transform the data for application GET requests on demand.
Registered: Sun Jun 16 00:44:34 UTC 2024 - Last Modified: Tue Apr 04 19:15:28 UTC 2023 - 7.6K bytes - Viewed (0) -
docs/select/README.md
(*) Parquet is disabled on the MinIO server by default. See below how to enable it. ## Enabling Parquet Format Parquet is DISABLED by default since hostile crafted input can easily crash the server. If you are in a controlled environment where it is safe to assume no hostile content can be uploaded to your cluster you can safely enable Parquet.
Registered: Sun Jun 16 00:44:34 UTC 2024 - Last Modified: Thu Sep 29 04:28:45 UTC 2022 - 6.5K bytes - Viewed (0) -
docs/docker/README.md
``` The command creates a new local directory `~/minio/data` in your user home directory. It then starts the MinIO container with the `-v` argument to map the local path (`~/minio/data`) to the specified virtual container directory (`/data`). When MinIO writes data to `/data`, that data is actually written to the local path `~/minio/data` where it can persist between container restarts. ### Windows ```sh docker run \ -p 9000:9000 \
Registered: Sun Jun 16 00:44:34 UTC 2024 - Last Modified: Thu Sep 29 04:28:45 UTC 2022 - 8.2K bytes - Viewed (0)